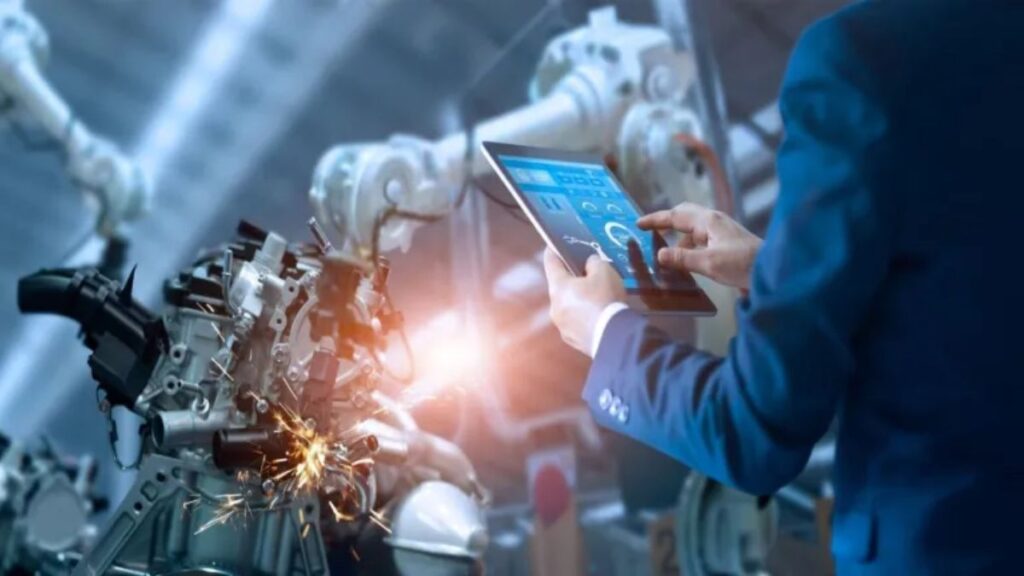
As the manufacturing and distribution landscape accelerates into the future, advanced technologies are fundamentally changing the way these industries operate. Facing rapidly evolving customer expectations and growing global competition, companies can no longer rely solely on traditional practices or incremental improvements. Instead, they are investing in new tools and platforms—ranging from advanced analytics and machine learning to interconnected devices and eco-friendly manufacturing processes—to streamline operations, ensure compliance, and gain an edge in the market. Leveraging tools such as artificial intelligence (AI), the Internet of Things (IoT), and robotics enables organizations to automate complex tasks, optimize supply chains, and respond quickly to shifts in demand. Furthermore, partnerships with trusted advisors, such as a top manufacturing accounting firm in the US, have become increasingly essential, helping businesses navigate this evolving terrain and maximize the benefits of digital transformation while minimizing risk.
Embracing next-generation solutions is essential not just for efficiency but as a strategic move to stay relevant amid constant disruption. Rapid innovation, consumer awareness, and regulation force manufacturers and distributors to adapt or risk obsolescence. From smart factories with 5G to circular economy principles, embracing technology boosts productivity and competitiveness. Companies investing in digital and sustainable strategies see short-term gains and long-term growth. These changes center on automation, connectivity, and sustainability, which not only optimize production but also foster innovation in business models, products, and customer experiences. Effectively using these technologies positions companies as industry leaders in a fast-paced, transparent, value-driven era. To future-proof operations, understanding how key technologies influence the modern industrial ecosystem is vital. Whether improving operations, scheduling, or global supply chains, adopting real-time data, predictive analytics, and automation drives success amid rapid change.
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
AI and machine learning are quickly becoming indispensable tools on the manufacturing floor and within distribution centers. Driven by exponential improvements in computing power and access to expansive datasets, these technologies now enable smarter workflows by analyzing vast amounts of production data to uncover inefficiencies, optimize schedules, and forecast machine maintenance needs before costly failures occur. Sophisticated algorithms can adapt to changing inputs and unexpected events, ensuring production quality and minimizing errors even in dynamic, high-mix environments. AI-powered vision systems, for example, can inspect products more accurately than the human eye, identifying subtle defects or inconsistencies and separating unusable items before they reach the consumer. This not only reduces costs and waste but also helps protect a manufacturer’s reputation by ensuring only high-quality products reach the market. As outlined by Forbes, integrating AI and machine learning throughout the production lifecycle—whether through demand planning, supply chain coordination, or predictive analytics—provides a powerful lever for efficiency and adaptability, especially in complex or highly customized manufacturing environments.
[suggestion]A simplified illustration of a modern factory with robotic arms, AI data analytics screens, IoT sensors, and green energy elements like solar panels, visually representing technology and sustainability working together.[/suggestion]
Internet of Things (IoT)
IoT has ushered in a new era of visibility and control in manufacturing. Sensors installed on machines and throughout supply chains now continuously gather and transmit real-time performance data, which organizations use to proactively manage assets and production lines. This wide-ranging visibility enables early detection of wear or malfunctions, helping engineers and managers prevent unplanned outages and reduce costly downtime. IoT-driven asset monitoring also significantly enhances safety, as sensors can alert personnel to hazardous conditions and ensure proper maintenance intervals. While only a small percentage of all industrial assets currently feature IoT connectivity, the adoption curve is rising steeply as costs fall and integration gets easier. Manufacturers are not only monitoring their equipment remotely. Still, they are also experimenting with augmented reality tools—such as smart glasses—allowing operators or technicians to access live instructions, repair manuals, or expert assistance, drastically reducing training times and production slowdowns. McKinsey highlights how these advancements are bridging the gap between digital theory and real-world execution, leading to new levels of accuracy, accountability, and tangible value throughout the enterprise.
Robotics and Automation
Modern robotics has evolved significantly, transforming manufacturing from reliance on simple, repetitive task machines to versatile, intelligent systems capable of performing highly complex assembly, inspection, and packaging tasks. Automation, driven by both robotics and software, eliminates repetitive manual processes, minimizes human error, and helps companies meet increasingly demanding production goals. Additionally, automation enhances workplace safety by taking over hazardous, strenuous, or otherwise undesirable jobs often associated with injuries or high turnover in the workforce. Today’s robotic solutions are no longer one-size-fits-all; instead, they are scalable and reconfigurable, giving manufacturers and distributors the flexibility to adjust production lines for new products or respond quickly to changes in market demand. According to Boston Business Journal, the integration of robotics is fueling faster turnaround times, supporting leaner inventories, and helping companies lower their per-unit costs, thus redefining how entire industries benchmark productivity and operational excellence.
Sustainability and Green Manufacturing
Manufacturers are under increasing pressure from customers, investors, and regulators to lower their environmental impact and operate more sustainably. The adoption of technologies that facilitate recycling, remanufacturing, and product design for disassembly is rapidly transitioning from a niche innovation to a standard industry practice. Manufacturers are investing in energy-efficient equipment, adopting renewable energy sources, and designing products that can be easily reused or recycled. Sustainability initiatives now encompass closed-loop manufacturing systems, real-time energy monitoring, and process improvements aimed at minimizing waste and reducing resource consumption. Circular economy principles, which prioritize maximizing the value of raw materials throughout a product’s lifecycle, not only protect the planet but also help companies reduce operational expenses and enhance brand trust. Early adopters of green manufacturing are already differentiating themselves and capturing market share, as noted by Harvard Business Review, by leveraging new business opportunities in markets that increasingly value environmental, social, and governance (ESG) standards within their supply chains.
Digital Twins and 5G Connectivity
Digital twins are virtual replicas of physical assets, processes, or plants that enable real-time simulation, monitoring, and optimization. They help engineers identify bottlenecks, test changes, and predict costs before implementation. This visual and predictive approach fosters continuous improvement, especially for high-value or complex manufacturing. As Globe Newswire notes, these digital tools reduce risk and speed innovation for global operations.
The emergence of 5G network slices complements this by offering high-bandwidth, reliable connectivity for modern factories. It supports autonomous robots, sensors, AI, and cloud analytics, enabling agile, data-driven decisions and seamless machine communication. According to CIO.com, this next-gen infrastructure underpins smart factories, unlocking automation, decentralized control, and integrated supply chains.
Conclusion
The manufacturing and distribution industries stand at a crossroads where innovation is the primary driver of success. Embracing advanced technologies—from AI and IoT to robotics, digital twins, and sustainable practices—is no longer optional for organizations seeking to thrive in the modern economy. Forward-thinking companies are leveraging these tools not only to reduce costs and increase operational flexibility but also to unlock new business models, service offerings, and sources of value. By prioritizing digital transformation and robust sustainability initiatives, industry leaders are building more resilient, adaptive, and growth-focused businesses. As this trend continues, those who invest in innovation today will be best equipped to meet future challenges and shape the next era of growth in manufacturing and distribution.